Understanding Genital Psoriasis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
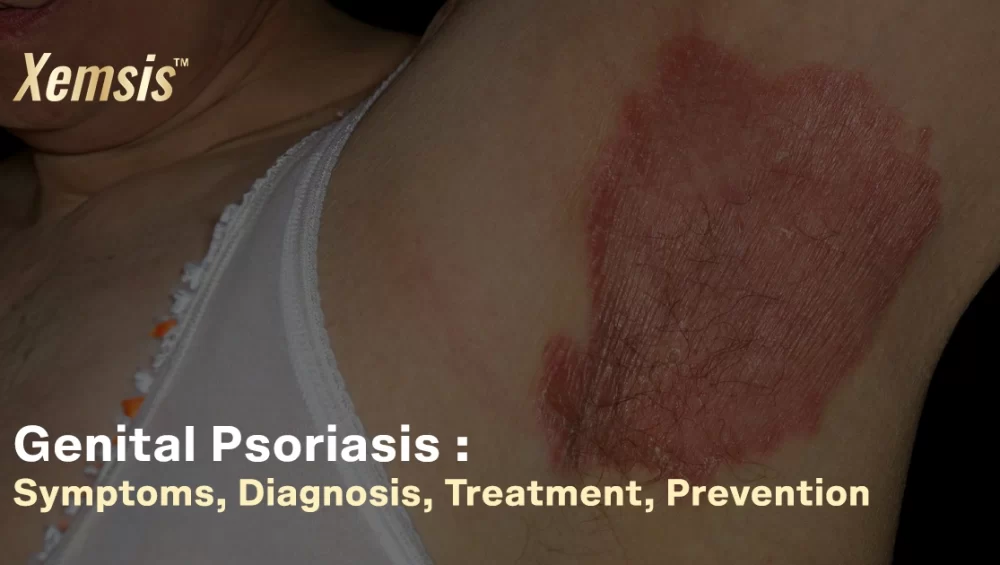
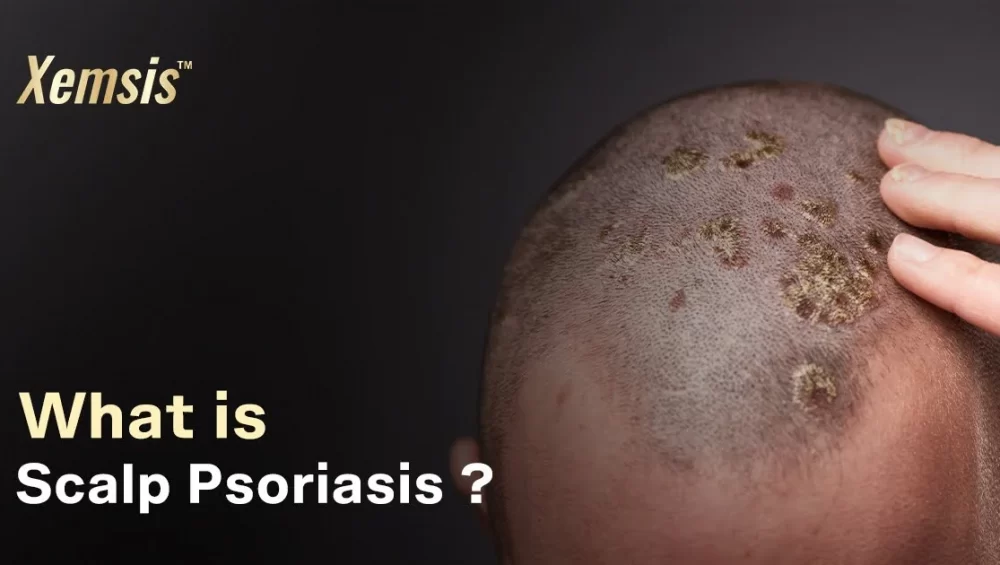
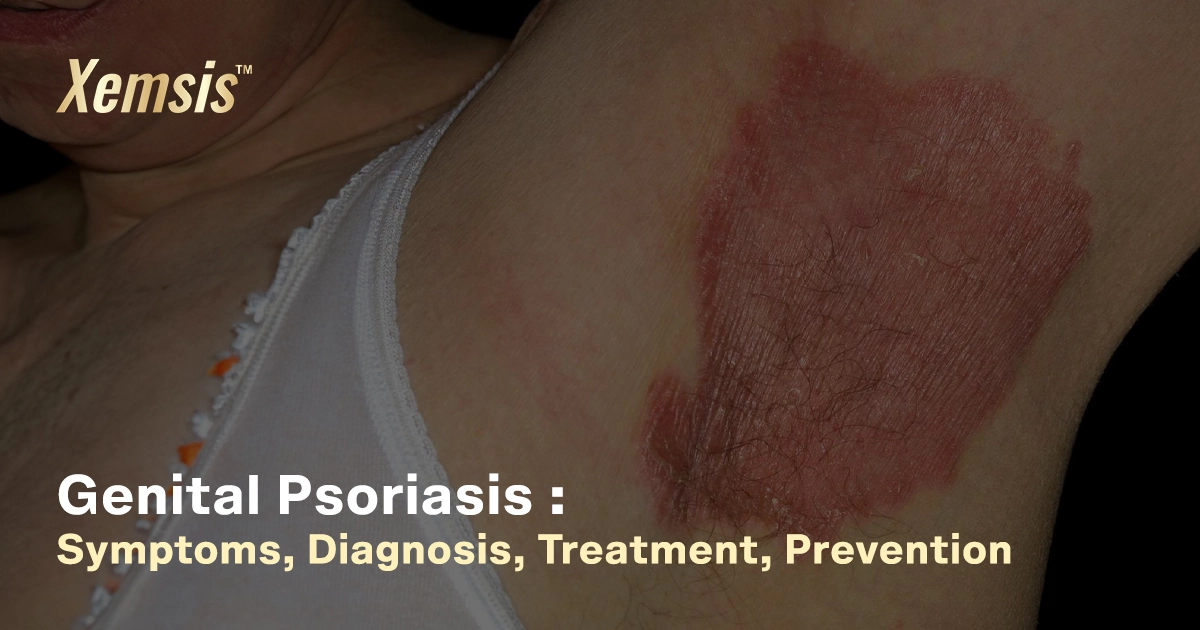
Genital psoriasis is an inflammatory auto-immune condition that causes smooth, flaky, and itchy patches on and around the genital areas that are painful. This condition ranges from mild to severe and is more difficult to manage than other forms of psoriasis, as genital areas are usually moist and sensitive. Genital psoriasis usually looks like a sexually transmitted disease or yeast infection and may affect the love life of the affected person. However, if you and your partner are comfortable, you can engage in sexual activities. It’s not contagious and can be managed effectively with proper treatments.Overview
What is genital psoriasis?
Genital psoriasis, also called vulvar, vaginal, or penile psoriasis, is a type of psoriasis that affects the genital areas like the groin, penis, vulva, creases between buttocks, pubis, and thighs. This condition is difficult to manage, so it is essential to consult a doctor.Who gets genital psoriasis?
Mostly, genital psoriasis affects people who already have other forms of psoriasis. But it can also affect people of any age who are without psoriasis. Research says that 63% of people suffering from psoriasis get genital psoriasis at least once in their lifetime.Is genital psoriasis the same as chronic psoriasis?
Chronic psoriasis is a common form of psoriasis, such as plaque psoriasis, that occurs in the skin as thick and scaly patches in various regions. Genetic psoriasis is a location-specific condition that occurs particularly in genital areas as shiny, flaky, and smooth patches. However, genital psoriasis is a form of chronic psoriasis that is slightly different from it in symptoms and treatments.What’s the difference between genital psoriasis and eczema?
Both eczema and genital psoriasis cause similar symptoms of reddish and itchy patches on the skin. Eczema is a common condition that can affect any region of the body, including the genitals. Genital psoriasis is a specific form of psoriasis that affects only the genital regions. Genital psoriasis mostly affects people who are already suffering from other forms of psoriasis, but eczema in the genital regions is mainly caused by genetics, poor environmental factors, or other infections. In terms of symptoms, genital psoriasis causes milder itching with a heavy burning sensation. On the other hand, eczema in genital regions causes only itching that is heavy and may even result in bleeding. It is very hard to differentiate these similar conditions on your own. Only experienced doctors can differentiate it thoroughly.Symptoms and Causes
Genital psoriasis symptoms
Symptoms of genital psoriasis include:- Thin, shiny, and smooth silvery scales in genital regions.
- The color of the affected skin is usually pink or red.
- The affected areas are cracked, causing itching, burning, and discomfort.
- Depending on the affected areas of the genital region, the skin may either be moist or dry.
- The silvery scales shed off as skin in genital areas rubs against each other when we move.
Causes of genital psoriasis
The exact cause of genital psoriasis has not been proven yet. However, having a family history of psoriasis can be transferred through genetics. Firstly, the immune system malfunctions in the body, attacking its healthy cells rapidly instead of foreign particles. This results in the rapid production of new skin cells, which grow faster than normal. So the body can’t shed dead cells as quickly as new cells grow. This results in the accumulation of dead cells that settle on the surface of the skin instead of shedding. The buildup of dead skin cells causes inflammation and forms psoriasis. Other than this, a lot of other conditions trigger genital psoriasis, including:- Overgrowth of yeast
- Skin injuries or microbial infections
- Friction from certain types of clothing fabrics
- Obesity
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Smoking
- Poor environmental factors
- Stress and
- Certain medications.
Is genital psoriasis contagious?
No. Genital psoriasis isn’t contagious. However, it may look similar to other skin conditions, like sexually transmitted diseases, eczema, yeast, or microbial infections. So it is essential to consult your doctor to identify the condition and get advice from him about your sexual health.Diagnosis and Tests
How is genital psoriasis diagnosed?
Doctors usually identify psoriasis by looking at the symptoms and medical history of your genetics. But as genital psoriasis looks similar to many other skin conditions, doctors may do a skin biopsy test to identify the condition exactly.Management and Treatment
How do you get rid of genital psoriasis?
As the skin around genital areas is very sensitive, the treatment is usually different from other forms of psoriasis.- Topical Medicines: Doctors provide effective ointments like xemsis, lotions, gels, or corticosteroid creams that reduce the inflammation of patches.
- Oral Drugs: If your symptoms are uncontrolled, doctors may provide medications like cyclosporine or infliximab. These medications may have complex dosages and side effects if taken over the long term. So doctors may recommend avoiding some food types. It’s crucial to follow their guidelines.
- Injections: To relieve you from excess pain and itching, doctors may recommend biological treatments or injections such as cyclosporine or methotrexate. These drugs have high dosages, so the medications should be followed only under the supervision of professional doctors.
How soon after treatment will I feel better?
Genital psoriasis is a long-lasting condition that has no proven cure. Following the medications regularly will reduce the severity of the symptoms. The severity of the condition, skin sensitivity, dosage of medications, and underlying medical conditions, if any, will determine the effectiveness of treatment. Also, it’s important to follow your doctor’s guidelines for avoiding certain things.Prevention
Can genital psoriasis be prevented?
There are no proven measures to prevent genital psoriasis. However, there are some ways to prevent new flare-ups.- Apply Xemsis regularly, as prescribed
- Maintaining a clean environment
- Using mild and chemical-free soaps that are recommended by doctors
- Moisturize your affected areas using pure coconut oil
- Wearing loose-fit pants and underwear
- Limiting shower times
- Managing stress
- Have a balanced diet with rich nutrients
- Avoid consuming alcohol and tobacco products
Living With Genital Psoriasis
When should I see my doctor?
You should visit your doctor without fail if:- Your symptoms are getting worse day by day
- You have severe pain and itching in the affected areas
- You experience discomfort while using toilets or having sex
- You are experiencing new medical conditions like nausea or fatigue.
What questions should I ask my doctor?
- Ask about the potential triggers and risk factors associated with your condition
- Ask about how you can manage your sexual activities. If you are comfortable, visit the doctor with your partner.
- Ask how often you should take your medications
- Ask about any possible side effects of your medications
- Ask how you can change your lifestyle to treat your condition more effectively
- Ask if there are any foods to be avoided
- Ask about warning signs so that you can be cautious about your condition
Conclusion
Genital psoriasis is a long-lasting condition that affects the sensitive genital areas and impacts the quality of life. Treatments and medications work in stages to relieve you of the condition. You may feel low self-esteem and embarrassment in public places. However, consistency in following the doctor’s guidelines, following the preventive measures regularly, and keeping hope is the best option to overcome this psoriasis.Reference
- National Library of Medicine: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6261118/
- National Psoriasis Foundation: https://www.psoriasis.org/genitals/
- Medical News Today: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/315217
- Healthline: https://www.healthline.com/health/genital-psoriasis#appearance
- WebMD: https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/psoriasis/genital-psoriasis-guide

Rakhul Mathivanan
Rakhul Mathivanan, a writer and filmmaker, focuses on creating innovative and unique content through directing short films, writing scripts, blogs, articles, case studies, and website content. He loves to watch movies, read books, listen to music, and travel. He has also had expertise in the field of writing and filmmaking for over a year and works closely with Xemsis by providing them with well-researched blogs about psoriasis.